Sustainability Due Diligence
At the core of our sustainability strategy is a robust due diligence framework that ensures we identify, assess, and address potential risks and impacts across our value chain. Through systematic risk assessments, monitoring, and stakeholder engagement, we work to uphold our environmental and social commitments while fostering transparency and accountability. We apply these processes to key areas, including climate change and other environmental concerns, human rights, and the practices of our service partners and suppliers.
We pay special attention to processes that inform strategic business decisions, such as mergers and acquisitions. For example, a Corporate Sustainability representative supports the Strategy team in systematically evaluating the social and environmental risks associated with potential joint ventures and acquisitions.
Our approach is guided by the principles outlined in key international instruments, standards and frameworks, including:
- ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 standards for environmental and energy management systems
- Task Force on Climate Related Financial Disclosures
- United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights (UNGPs)
- OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises
- European Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive
- Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR)
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
- International Covenant on Economic, Social, and Cultural Rights
- The Core Labor Conventions of the International Labor Organization (ILO)
Human Rights Due Diligence
dormakaba acknowledges its responsibility to respect human rights as outlined in the UNGPs. We aim to lead by example and collaborate with partners to promote eco-friendly practices and protect human rights. As the world becomes more interconnected, there is growing public focus on how companies respect human rights within their operations and value chains. Businesses must show they uphold human dignity and welfare while creating jobs, wealth, and growth for all communities. Human rights apply to everyone, regardless of nationality, gender, ethnicity, or other characteristics, and are interrelated, interdependent, and indivisible.
Our aim is to conduct Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD) across our business to proactively assess, identify, prevent, and mitigate actual and potential adverse human rights impacts on potentially affected rights-holders throughout the value chain. HRDD also helps us find opportunities to support and promote the exercise of fundamental human rights.
Human Rights Due Diligence (HRDD) process
Policy commitment
Our commitment to human rights is anchored in the dormakaba Statement of Commitment on Human Rights, which defines our salient issues, outlines our due diligence approach, and applies across our entire value chain. It is supported by additional directives (Responsible Labor and Zero Recruitment Fees Directive), the Supplier Code of Conduct, the dormakaba Code of Conduct, the Statement of Commitment on Responsible Minerals Sourcing for high-risk minerals, the Material Compliance Directive and the Sustainable Procurement Directive.
Assessing actual and potential impacts to define salient issues
dormakaba does not attribute more importance to one human right over another. However, for the implementation of our human rights commitment, dormakaba prioritizes human rights issues that are most salient to the business — identified via a formal human rights saliency assessment conducted in accordance with the UNGPs. The saliency assessment also considered environmental matters.
This included consultations with 20 key internal and external stakeholders, such as human rights experts, customers, and suppliers, which generated a focused list of salient human rights issues for dormakaba.
Saliency was determined based on the inherent human rights risk, without considering how well our company currently manages the issue. Thirteen issues appeared as most relevant, and these were further analyzed in terms of the company’s leverage and the potential severity of impact. Severity here is defined as the scale, scope, and irremediability of the potential human rights impacts.
dormakaba Human Rights Saliency Matrix
Among the broader human rights issues identified, we commit to focusing on the salient human rights issues defined below (in alphabetical order):
|
Salient issue |
|
Potential human rights impacts |
|
Illustrative example in our value chain (not exhaustive) |
|
Child labor |
|
Rights on the protection of the child; Right to a family life; Right to an education |
|
Child labor used for cobalt and mica mining. |
|
Contributing to conflict |
|
Right to the security of the person; Freedom from cruel, inhumane, and degrading treatment |
|
Sourcing raw materials from conflict zones and therefore indirectly financing armed conflicts. |
|
Customer safety |
|
Right to health |
|
Door not stopping during operation and injuring someone, or not opening in the event of fire and leading to a fatality. |
|
Environmental issues impacting human rights |
|
Right to safe and clean drinking water and sanitation; Right to health; Right to an adequate standard of living |
|
Bauxite mine polluting water used by local communities for drinking, washing, and cooking. |
|
Migrant workers (forced labor) |
|
Right not to be subjected to slavery, servitude, or forced labor; Right to freedom of movement |
|
Migrant workers in plants hired through recruitment agencies at risk of modern slavery/bonded labor. |
|
Outsourced services |
|
Right to health; Right to enjoy just and favorable conditions of work |
|
Outsourced/subcontracted employees in plants facing health and safety risks (e.g., cleaning and security staff). |
|
Occupational health & safety |
|
Right to health; Right to enjoy just and favorable conditions of work; Right to social security, including social insurance |
|
Staff installing products on behalf of dormakaba facing injury risks: lifting heavy equipment, unsafe construction sites, road accidents, etc. |
Due to limited transparency in the value chain and the fact that the importance of issues may evolve, our salient issues are analyzed annually through human rights impact assessments or social audits in high-risk areas, incorporating feedback from internal and external stakeholders — for example through workers interviews and workers surveys of subcontractors and our own staff — as well as expert insights.
Integrate findings and take appropriate action
We develop prevention and mitigation measures based on identified human rights risks, integrating them into our operations, trainings, policies, and management systems through a human rights roadmap approved by our Executive Committee. This roadmap assigns responsibilities and is reviewed annually. We are committed to ongoing dialogue with internal and external stakeholders to continuously improve our HRDD and, where our influence is limited, work to increase our impact through collaboration with key partners, including employees, suppliers, civil society, and businesses.
Details on actions taken in FY 24/25 based on HRDD-related findings are found in the Own Workforce and Workers in the Value Chain chapters.
Tracking and communicating performance
We are committed to transparently reporting on the progress of our efforts in our annual sustainability report and publicly accounting for how human rights issues are addressed.
We track the effectiveness of our actions and influence to ensure human rights are respected in the value chain. We do this through a management system with concrete targets and KPIs, monitoring the implementation of the human rights road map.
We also issue an annual Modern Slavery and Child Labor Statement that sets out what we are doing to ensure that slavery, human trafficking, and child labor are not taking place in our supply chains or any part of the business. The statement lays out the strategy and actions that outline our compliance with the ILO Conventions 138 and 182, the ILO-IOE Child Labor Guidance Tool for Business, and the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights1.
Remediating adverse impacts
When adverse human rights impacts caused by our business activities or linked to our operations are discovered, we are committed to taking timely and transparent action to remediate them in a fair and equitable manner in line with the UNGPs. Where we identify impacts linked to our business relationships, we will use our influence to encourage suppliers and business partners to respect human rights. You can learn more about our actions in the Own Workforce and Workers in the Value Chain chapters.
Access to grievance
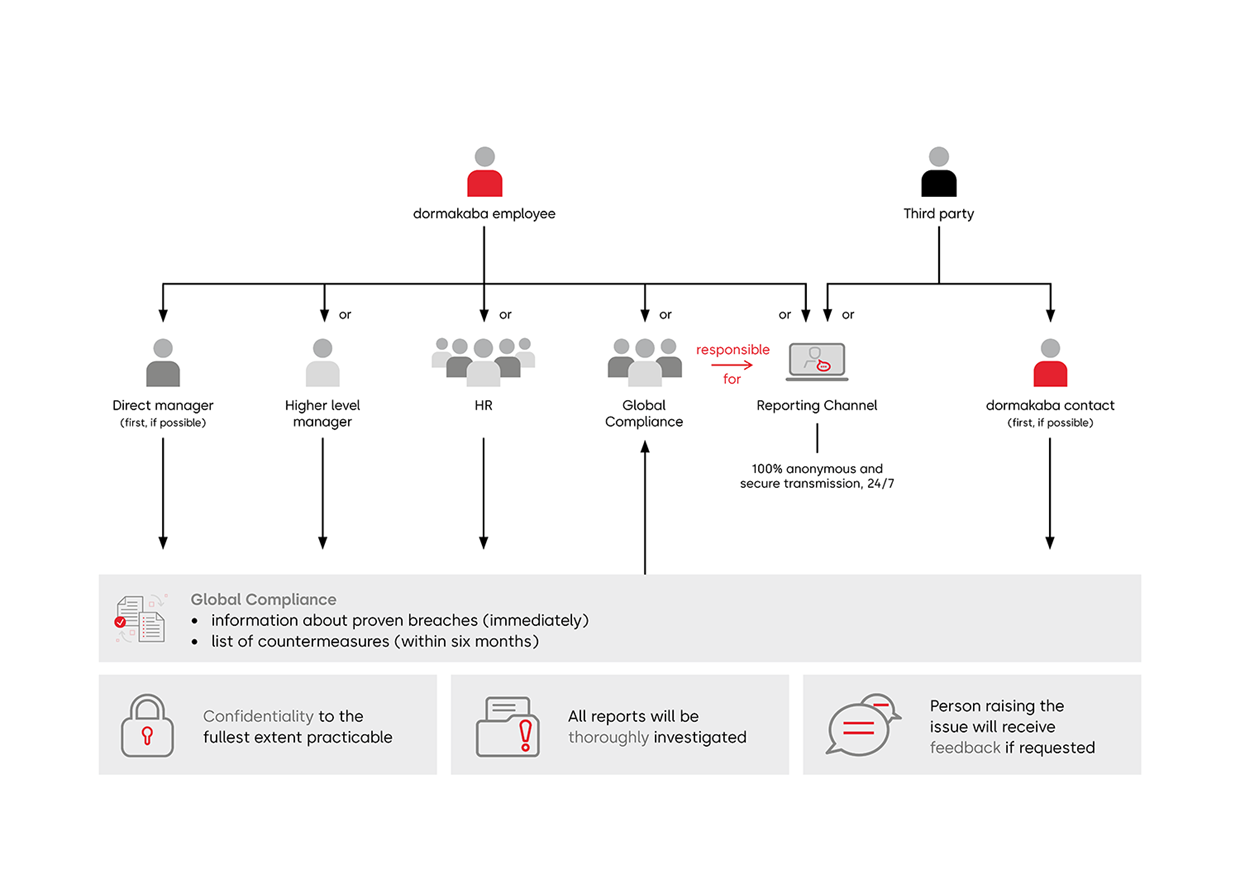
The CoC outlines the procedure for reporting grievances or legal breaches. Our global whistleblowing tool is available 24/7 in nine languages for both internal and external stakeholders, providing an initial response within two to three days and regular updates if anonymous communication is set up. We aim to foster a culture where employees feel encouraged to voice concerns.
Global Compliance reviews all notifications, creates action plans when necessary, and tracks remediation progress, which may involve legal advice, external experts, investigations, or training. The CEO and Executive Committee may be involved if needed. Compliance cases are reported regularly to the Executive Committee.
Before launching the tool, we gathered feedback from stakeholders, including the German Works Council and HR representatives, to ensure protection from retaliation. The tool largely meets the effectiveness criteria set out in the UNGPs, and complies with the German Supply Chain Due Diligence Act.
We launched a communication campaign to familiarize employees with the tool, including posters for production workers. Our Code of Conduct, Supplier Code of Conduct and the pre-departure phase training package for foreign migrant workers also include a detailed description of our reporting channels. A training campaign on the Code of Conduct was carried out in the FY 24/25, with 9,367 employees (59%) participating.
We gather whistleblower feedback on the toolʼs design, such as accessibility, and incorporate it into regular system updates. The Global Compliance department monitors the implementation of agreed remediation measures.
Environmental Due Diligence
Our company is committed to conducting robust environmental due diligence by implementing internationally recognized frameworks that support the proactive identification, assessment, and management of environmental and climate-related risks and opportunities. Through the application of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management System), and ISO 50001 (Energy Management System), we ensure that environmental considerations are fully integrated into our governance, risk management, and strategic planning processes.
These standards enable us to reduce environmental impacts, enhance energy efficiency, and effectively manage climate-related risks — supporting long-term sustainability and resilience in a rapidly changing world. Currently, 68% of our manufacturing plants are ISO 14001 certified, and 19% are ISO 50001 certified.
Governance and accountability
Environmental due diligence begins with strong governance. ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 require local management to take a leading role in setting environmental and energy objectives, ensuring appropriate resources are available, and promoting continual improvement. Similarly, by following TCFD recommendations, we clearly disclose the governance structures in place for overseeing sustainability and climate-related risks and opportunities, including board-level oversight and managementʼs role in assessing and managing these issues.
Risk identification and management
A fundamental part of our environmental due diligence is the identification and management of environmental and climate-related risks. ISO 14001 requires the evaluation of environmental aspects and their potential impacts under both normal and abnormal conditions. ISO 50001 adds to this by requiring a comprehensive energy review to identify significant energy uses and inefficiencies. These are integrated into operational controls and improvement objectives.
Read about our climate-related risks and opportunities and scenario analysis in the Climate Change chapter.
The TCFD framework complements this by focusing on climate-related risks and opportunities, particularly physical risks (e.g., extreme weather events) and transition risks (e.g., policy and market changes). Through scenario analysis, we assess the resilience of our strategy under different climate futures, helping us anticipate and mitigate long-term impacts.
At the asset level, local operations leaders are responsible for reporting environmental and climate-related risks identified through their ISO 14001 management systems into the company’s broader enterprise risk management system, while the results from the climate change scenario analysis are reported there by Corporate Sustainability.
Additionally, through ISO 14001 and ISO 50001 processes, we identify locally applicable environmental and energy-related legislation and the incorporate these requirements into operational and compliance processes, thereby reducing regulatory risk.
Further information about how climate-related risks and opportunities are integrated in dormakaba’s overarching enterprise risk management system is found in the General Information chapter.
Performance monitoring and continuous improvement
To maintain environmental due diligence over time, we have established robust performance monitoring and continuous improvement processes. Both ISO standards are built around the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle, which ensures that our environmental and energy performance is regularly measured, evaluated, and improved. The TCFD framework supports this by requiring the use of relevant metrics and targets to assess climate-related risks and opportunities, thereby promoting accountability and informed decision-making.
Transparency and stakeholder engagement
Finally, transparency and stakeholder engagement are central to our approach. By aligning with the TCFD recommendations, we provide clear, consistent, and comparable disclosures of our climate-related risks and performance. This not only builds trust with investors, regulators, and the public but also demonstrates our commitment to responsible environmental stewardship.